1878. Get Biggest Three Rhombus Sums in a Grid
Problem
Tags: Array, Math, Sorting, Heap (Priority Queue), Matrix, Prefix Sum
You are given an m x n integer matrix grid.
A rhombus sum is the sum of the elements that form the border of a regular rhombus shape in grid. The rhombus must have the shape of a square rotated 45 degrees with each of the corners centered in a grid cell. Below is an image of four valid rhombus shapes with the corresponding colored cells that should be included in each rhombus sum:
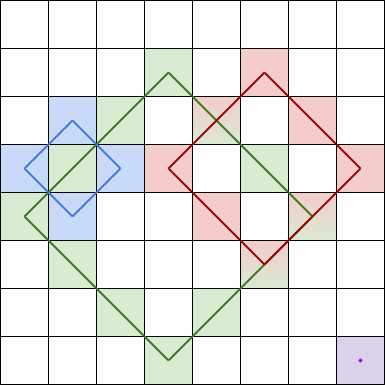
Note that the rhombus can have an area of 0, which is depicted by the purple rhombus in the bottom right corner.
Return the biggest three distinct rhombus sums in the grid in descending order__. If there are less than three distinct values, return all of them.
Example 1:
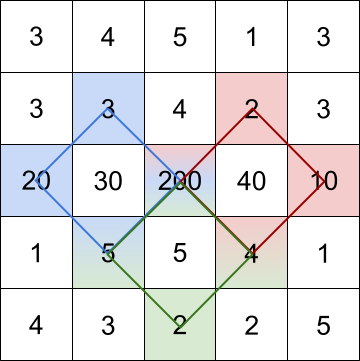
Input: grid = [[3,4,5,1,3],[3,3,4,2,3],[20,30,200,40,10],[1,5,5,4,1],[4,3,2,2,5]]
Output: [228,216,211]
Explanation: The rhombus shapes for the three biggest distinct rhombus sums are depicted above.
- Blue: 20 + 3 + 200 + 5 = 228
- Red: 200 + 2 + 10 + 4 = 216
- Green: 5 + 200 + 4 + 2 = 211
Example 2:
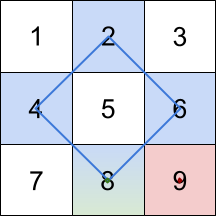
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
Output: [20,9,8]
Explanation: The rhombus shapes for the three biggest distinct rhombus sums are depicted above.
- Blue: 4 + 2 + 6 + 8 = 20
- Red: 9 (area 0 rhombus in the bottom right corner)
- Green: 8 (area 0 rhombus in the bottom middle)
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[7,7,7]]
Output: [7]
Explanation: All three possible rhombus sums are the same, so return [7].
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 501 <= grid[i][j] <= 10^5
Code
CPP
// 1878. Get Biggest Three Rhombus Sums in a Grid (10/5/53378)
// Runtime: 84 ms (92.65%) Memory: 20.70 MB (80.88%)
#define rang(a) begin(a), end(a)
template <class T, class C = less<typename T::value_type>>
void sort(T &a, C c = C()) {
sort(rang(a), c);
}
template <class T> void uniq(T &a) {
sort(a), a.erase(unique(rang(a)), end(a));
}
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getBiggestThree(vector<vector<int>>& a) {
static int s1[110][110],s2[110][110];
int n=a.size(),m=a[0].size();
for(int i=0;i<n+5;++i)
for(int j=0;j<m+5;++j)
s1[i][j]=s2[i][j]=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)
for(int j=0;j<m;++j){
s1[i+1][j+1]=s1[i][j]+a[i][j];
}
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)
for(int j=m-1;j>=0;--j){
s2[i+1][j+1]=s2[i][j+2]+a[i][j];
}
vector<int>tmp;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)
for(int j=0;j<m;++j){
for(int k=0;;++k){
int i2=i+k;
int j2=j+k;
if(i2>=n||j2>=m)break;
int i3=i-k;
int j3=j+k;
if(i3<0)break;
int i4=i;
int j4=j+k+k;
if(j4>=m)break;
if(k==0)tmp.push_back(a[i][j]);
else{
tmp.push_back(s1[i2+1][j2+1]-s1[i][j]+s1[i4+1][j4+1]-s1[i3][j3]+s2[i+1][j+1]-s2[i3][j3+2]+s2[i2+1][j2+1]-s2[i4][j4+2]-a[i][j]-a[i2][j2]-a[i3][j3]-a[i4][j4]);
}
}
}
uniq(tmp);
reverse(begin(tmp),end(tmp));
while(tmp.size()>3)tmp.pop_back();
return tmp;
}
};